Are you wondering which health issue is associated with malnutrition? Malnutrition, a condition caused by an inadequate intake of essential nutrients, is often associated with images of undernourished children in developing countries. However, malnutrition is not limited to such settings and can affect people of all ages, genders, and socioeconomic backgrounds, even in developed countries.
Malnutrition can manifest in various forms, including undernutrition, overnutrition, and micronutrient deficiencies, and can have severe health consequences. In this article, we will explore the hidden health consequences of malnutrition and shed light on the link between nutritional deficiency and various health issues.
Undernutrition – A Hidden Threat to Health

Undernutrition, or protein-energy malnutrition, occurs when the body does not receive adequate calories, protein, and other essential nutrients to meet its energy and growth requirements. It can result from insufficient food intake, poor absorption of nutrients, or increased nutrient losses due to illness or injury. Undernutrition can have serious health consequences, affecting various organ systems in the body.
1.1 Impaired Growth and Development
One of the undernutrition’s most noticeable health consequences is impaired growth and development, especially in children. Insufficient protein intake and other essential nutrients during early childhood can lead to stunted growth, characterized by short stature and reduced muscle mass. Stunting affected physical growth and cognitive development, leading to poor academic performance and reduced earning potential in adulthood.
1.2 Weakened Immune System
Malnutrition weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and diseases. Protein-energy malnutrition can reduce the production of antibodies, which are crucial for fighting infections. This makes undernourished individuals more vulnerable to common illnesses such as respiratory infections, diarrhoea, and other infections, which can be life-threatening, particularly in children and older adults.
1.3 Nutrient Deficiencies
Undernutrition can also result in various nutrient deficiencies, such as iron, vitamin A, vitamin D, and zinc. These deficiencies can have serious health consequences. For example, iron deficiency can lead to anaemia, which causes fatigue, weakness, and impaired cognitive function. Vitamin A deficiency can lead to night blindness and increased vulnerability to infections. Vitamin D deficiency can result in weakened bones, increasing the risk of fractures, while zinc deficiency can impair immune function and growth.
1.4 Increased Mortality Risk
Undernutrition increases mortality risk, particularly among vulnerable populations such as children under five and older adults. It weakens the body’s ability to fight infections and recover from illnesses, leading to higher mortality rates. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), malnutrition contributes to 45% of all child deaths globally, making it a leading cause of mortality among children under five.
Also Read. Can Hair Color be Used Without Developer? | All You Need to Know
Overnutrition – A Modern Epidemic
While undernutrition is a well-known health issue associated with malnutrition, overnutrition, or excessive intake of calories, it is also becoming a significant health concern worldwide. Overnutrition is often associated with a high intake of energy-dense, nutrient-poor foods, leading to weight gain and obesity. Obesity is a growing epidemic and is associated with numerous health issues.
2.1 Obesity and Related Health Issues
Obesity increases the risk of developing several chronic health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, musculoskeletal disorders, and respiratory issues. Excess body weight strains the heart, leading to increased blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels, and an increased risk of heart disease. Obesity also disrupts glucose metabolism, leading to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, characterized by high blood sugar levels.
Additionally, obesity is linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancer, such as breast, colon, and prostate cancer. Musculoskeletal disorders, such as osteoarthritis, are also more common in individuals who are overweight or obese due to increased stress on the joints. Respiratory issues, including sleep apnea and asthma, are also associated with obesity, as excess weight can affect lung function and increase inflammation in the airways.
2.2 Psychological and Social Consequences
Overnutrition and obesity can also have significant psychological and social consequences. Obesity is often associated with stigma, discrimination, and poor body image, leading to low self-esteem, depression, anxiety, and social isolation. These psychological and social consequences of obesity can further impact an individual’s overall health and well-being, leading to a reduced quality of life.
Micronutrient Deficiencies – The Hidden Culprit
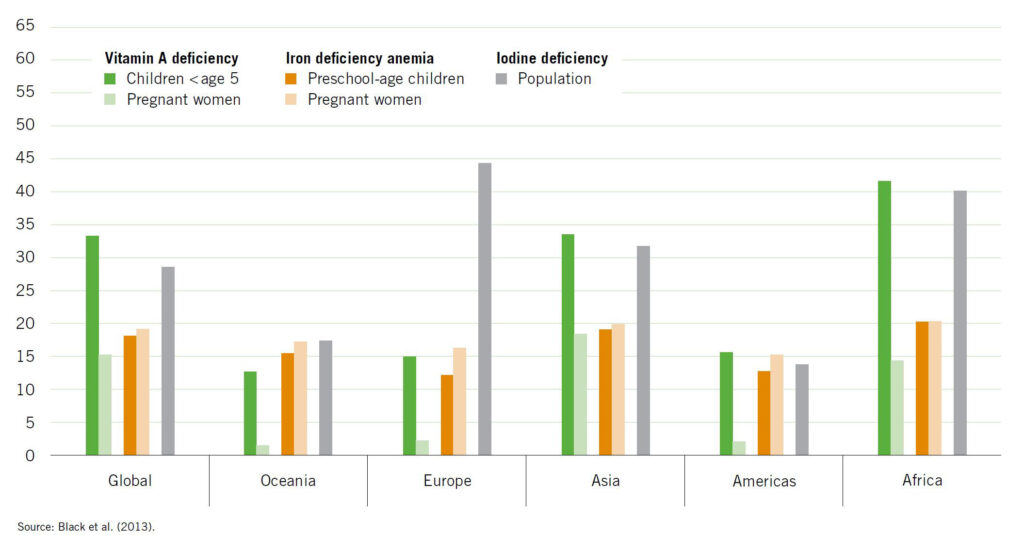
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are essential for the proper functioning of the body. Micronutrient deficiencies, also known as hidden hunger, occur when the body does not get enough of these essential nutrients, leading to various health issues.
3.1 Impact on Cognitive Function
Micronutrient deficiencies can significantly impact cognitive function, particularly in children. Adequate intake of vitamins and minerals is crucial for brain development and cognitive abilities, such as learning, memory, and problem-solving. Deficiencies in nutrients such as iron, iodine, vitamin B12, and folate can impair cognitive function and lead to developmental delays, poor academic performance, and reduced adult earning potential.
3.2 Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases
Micronutrient deficiencies can also increase the risk of chronic diseases. For example, vitamin D deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of osteoporosis, characterized by weakened bones. Iron deficiency can lead to anaemia, associated with fatigue, weakness, and impaired immune function. Iodine deficiency can result in thyroid disorders, while vitamin C deficiency can lead to scurvy, a condition characterized by weakness, gum bleeding, and poor wound healing. These micronutrient deficiencies can have long-term health consequences and impact an individual’s well-being.
Which health issue is associated with malnutrition brain?
Malnutrition, a lack of proper nutrition, can have various health issues. Here are some common health issues that can arise due to malnutrition:
Stunted Growth: Malnutrition, especially during childhood, can lead to stunted growth, both in terms of height and weight. Proper nutrition is crucial for children’s optimal growth and development, and inadequate intake of essential nutrients like proteins, vitamins, and minerals can impair growth.
Weakened Immune System: Malnutrition can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and diseases. Essential nutrients like vitamins A, C, D, and zinc are crucial for a healthy immune system. Their deficiency due to malnutrition can compromise the body’s ability to fight off infections.
Cognitive Impairment: Malnutrition can have detrimental effects on cognitive function, including impaired memory, reduced attention span, and learning difficulties. Adequate nutrition, especially during early childhood, when the brain is developing rapidly, is essential for optimal cognitive development.
Anaemia: Malnutrition can lead to anaemia, a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells or haemoglobin in the blood. Lack of key nutrients like iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid, essential for producing healthy red blood cells, can result in anaemia.
Muscle Wasting: Malnutrition can cause muscle wasting or muscle atrophy, which is the loss of muscle mass and strength. Inadequate intake of proteins, which are essential for muscle building and repair, can result in muscle wasting, leading to weakness and reduced physical performance.
Bone and Teeth Problems: Malnutrition can also affect bone and teeth health. Lack of essential nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus can lead to weak bones and teeth, making individuals more prone to fractures, dental cavities, and other dental issues.
Organ Dysfunction: Malnutrition can result in organ dysfunction, as the body may not receive enough nutrients to support the proper functioning of organs such as the liver, kidneys, and heart. This can lead to various health problems and complications.
It’s important to note that malnutrition can have long-term and irreversible effects on overall health, growth, and development. It can affect individuals of all ages, but it is particularly harmful during critical periods of growth and development, such as pregnancy, infancy, and childhood.
Proper nutrition, with a well-balanced diet containing all essential nutrients, is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing malnutrition-related health issues. If you suspect malnutrition in yourself or someone else, seeking medical advice for proper diagnosis and management is important.
Conclusion:
Malnutrition, in its various forms of undernutrition, overnutrition, and micronutrient deficiencies, can have severe hidden health consequences. It can impact growth and development, weaken the immune system, lead to nutrient deficiencies, increase the risk of chronic diseases, and have psychological and social consequences.
Recognizing and addressing the link between nutritional deficiency and health issues is crucial for improving overall health and well-being in developing and developed countries. Efforts to prevent and address malnutrition should include promoting healthy and balanced diets, improving access to nutritious foods, and raising awareness about the importance of adequate nutrition for overall health. By addressing the hidden health consequences of malnutrition, we can strive towards a healthier and more nourished global population.
FAQs!
What health issue is associated with malnutrition?
Stunted growth and development: Malnutrition, especially during early childhood, can lead to impaired growth and development, resulting in shorter height, reduced muscle mass, and delayed cognitive development.
Weakened immune system: Malnutrition weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, diseases, and other health complications.
Nutrient deficiencies: Malnutrition can result in various nutrient deficiencies, such as vitamin and mineral deficiencies, which can lead to problems like anaemia, weak bones, impaired vision, and skin disorders.
Muscle wasting and weakness: Malnutrition can cause muscle wasting and weakness, leading to reduced strength, mobility, and overall physical function.
Organ damage: Severe and prolonged malnutrition can cause damage to internal organs, including the heart, liver, and kidneys, leading to organ dysfunction and failure.
How does malnutrition affect children?
Malnutrition can have severe and long-lasting effects on children’s health, including:
Poor growth and development: Malnutrition during early childhood can result in stunted growth, delayed motor skills, and impaired cognitive development, which can have lifelong consequences.
Increased susceptibility to infections: Malnourished children are more prone to infections like diarrhoea, respiratory infections, and other diseases, which can further compromise their health and well-being.
Developmental delays: Malnutrition can delay the physical, mental, and emotional development of children, leading to challenges in learning, socializing, and overall functioning.
Weakened immune system: Malnutrition weakens the immune system, making children more susceptible to illnesses and infections, leading to frequent hospitalizations and increased mortality rates.
Long-term health risks: Malnutrition in childhood can increase the risk of developing chronic health conditions in adulthood, such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
How does malnutrition affect the elderly?
Malnutrition can have serious implications for the health and well-being of elderly individuals, including:
Muscle wasting and weakness: Malnutrition can cause muscle wasting and weakness in the elderly, reducing strength and mobility and increasing the risk of falls and fractures.
Nutrient deficiencies: Malnutrition can result in nutrient deficiencies in the elderly, leading to problems like osteoporosis, anaemia, and impaired cognitive function.
Reduced immunity: Malnutrition weakens the immune system in the elderly, making them more susceptible to infections and illnesses, which can lead to prolonged hospitalization and increased mortality rates.
Delayed wound healing: Malnutrition can impair the healing of wounds and injuries in the elderly, leading to an increased risk of infections and complications.
The decline in overall health: Malnutrition can lead to a decline in overall health and functional abilities in the elderly, leading to reduced quality of life, increased dependency on caregivers, and increased healthcare costs.
Can malnutrition be reversed?
Yes, in many cases, malnutrition can be reversed with appropriate interventions, such as:
Nutritional rehabilitation: Providing adequate and balanced nutrition through a well-balanced diet, fortified foods, and nutritional supplements can help reverse malnutrition.
Medical treatment: Treating underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to malnutrition, such as infections, digestive disorders, or hormonal imbalances, can help improve nutrient absorption and utilization.
Counselling and education: Providing counselling and education on healthy eating practices, food preparation, and dietary management can help individuals make informed choices about their nutrition.
