Will Infection Show in Blood Test? Medical professionals commonly use blood tests to diagnose various health conditions, including infections. But how do blood tests work in detecting infections? Can all infections be detected through blood tests? Several blood tests can detect infections, including bacterial and viral infections.
Some of the most common blood tests to detect infections include tests for bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae and viral infections like the common cold. In this article, we will delve into the world of blood tests and explore how they can be used to detect infections, including their limitations and benefits.
What Are Blood Tests?
Blood tests, also known as blood screenings or blood work, are laboratory tests that analyze a blood sample to assess a person’s overall health or diagnose specific medical conditions. Blood is a vital fluid in our body that carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products. It also contains cells, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, which play crucial roles in various physiological processes.
Blood tests can provide valuable information about a person’s health status, including organ function, nutrient levels, and infections or diseases. They are performed by drawing a small amount of blood from a vein, usually in the arm, and sending it to a laboratory for analysis. Blood tests are commonly used in routine check-ups, disease screening, and monitoring treatment efficacy.
How Do Blood Tests Detect Infections?
Blood tests can detect infections caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi. When the body is infected, the immune system produces specific proteins called antibodies, which help fight off the invading pathogens. Blood tests can detect these antibodies or other markers of infection in the blood sample, indicating the presence of an infection.
Depending on the suspected infection and the information needed, several blood tests can be used to detect infections. Some common blood tests used to detect infections include:
Complete Blood Count (CBC):
This test measures the levels of different types of cells in the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. An increase or decrease in certain types of white blood cells can indicate an infection. A dip in white blood cell counts can indicate an infection, such as the common cold or the flu.
C-reactive Protein (CRP):
CRP is a protein produced by the liver in response to inflammation, including that caused by infections. Elevated CRP levels in the blood can indicate the presence of an infection. There is no definitive CRP test, but a few common ones are used in medical practice. The most common CRP test is the serum CRP test. This test measures the amount of CRP in a blood sample.
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR):
ESR measures how quickly red blood cells settle at the bottom of a test tube. Higher ESR levels can indicate inflammation, including that caused by infections. ESR is a blood test that measures the speed at which red blood cells settle in a test tube. Higher ESR levels can indicate inflammation, including that caused by infections.
Blood Cultures:
This test involves growing bacteria or other microorganisms from a blood sample to identify the type of infection and determine the most effective treatment. A blood test can identify the type of infection and determine the most effective treatment.
Serology Tests:
These tests detect specific antibodies the immune system produces in response to an infection. For example, IgM antibodies in the blood can indicate a recent or active infection, while IgG antibodies can indicate a past infection or immunity.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Tests:
PCR is a highly sensitive and specific test that can detect the genetic material of pathogens, such as viruses or bacteria, in the blood. PCR tests commonly diagnose viral infections like HIV, hepatitis, or COVID-19. A PCR test is a specific and sensitive test that can detect the genetic material of pathogens, such as viruses or bacteria, in the blood. PCR tests commonly diagnose viral infections like HIV, hepatitis, or COVID-19.
Also Read. The Benefits of Using a Jade Roller: Improve Skin Health and Reduce Inflammation
Limitations of Blood Tests for Infections:
While blood tests are valuable tools for detecting infections, they are not always foolproof. There are some limitations to consider when interpreting the results of blood tests for infections:
False Negative Results:
Blood tests may not always detect an infection, especially in the early stages or if the infection is localized in a specific body part. For example, a blood culture may be negative if the infection is limited to a certain organ or tissue and not present in the bloodstream.
False Positive Results:
On the other hand, blood tests may also yield false positive results, indicating an infection when there may not be one. This can occur due to various reasons, such as cross-reactivity with other antibodies or the presence of autoantibodies in the blood, which can interfere with the accuracy of the test.
Limited Detection of Non-Bloodborne Infections:
Blood tests are effective in detecting infections that are present in the bloodstream. Still, they may be unable to detect infections localized in other parts of the body, such as the respiratory, urinary, or gastrointestinal tract. Other tests, such as imaging studies or specific diagnostic procedures, may be required for a definitive diagnosis.
Timing of Testing:
The timing of blood tests for infections can also affect the accuracy of the results. Some blood tests may not yield accurate results if performed too early or late during infection. For example, serology tests may not detect antibodies in the early stages of infection, while PCR tests may yield false negative results if the viral load in the blood is low.
Interpretation of Results:
Interpreting blood test results for infections requires expertise and consideration of various factors, such as the patient’s clinical presentation, medical history, and other diagnostic findings. False interpretations can lead to misdiagnosis or unnecessary treatments, highlighting the importance of clinical judgment and appropriate follow-up testing, if needed.
Benefits of Blood Tests for Infections:

Despite the limitations, blood tests are valuable tools in detecting infections and have several benefits:
Early Detection:
Blood tests can help in the early detection of infections, allowing for timely intervention and management. Early diagnosis and treatment of infections can prevent complications and improve patient outcomes. A chest X-ray is a common test used to look at the lungs. It can help in the early diagnosis of infections, allowing for timely intervention and management. Early diagnosis and treatment of infections can prevent complications and improve patient outcomes.
Monitoring Treatment Efficacy:
Blood tests can be used to monitor the response to treatment for infections. Changes in blood markers, such as decreasing antibody levels or resolving inflammation, can indicate the effectiveness of the treatment. A blood marker test is a medical test that measures the levels of specific substances in the blood. Blood markers are used to monitor the response to treatment for infections. Changes in blood markers, such as decreasing antibody levels or resolving inflammation, can indicate the effectiveness of the treatment.
Non-Invasive:
Blood tests are generally non-invasive and do not require extensive preparation or special equipment. They are relatively easy to perform and are widely available in most healthcare settings. Blood tests can examine several aspects of a person’s health, including blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
Wide Range of Infections:
Blood tests can detect various infections caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi, making them versatile in diagnosing various infections. A few different types of blood tests can be used to detect various infections. Bacterial blood tests can detect bacteria, such as Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and E. coli.
Conclusion:
Blood tests are valuable tools for detecting infections and providing important information for diagnosing, treating, and monitoring infections. However, they have limitations, including the possibility of false results, limited detection of non-bloodborne infections, the timing of testing, and interpretation of results.
Healthcare professionals must consider these limitations and use clinical judgment with blood test results for accurate diagnosis and management of infections.”
FAQs!
Will a blood test show if I have an infection?
Yes, a blood test can help determine if you have an infection. Blood tests are commonly used to detect the presence of infection-causing organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, or parasites, in the body. The specific type of blood test ordered will depend on the suspected infection and the symptoms you are experiencing.
What types of blood tests are used to detect infections?
Several types of blood tests can be used to detect infections, including:
Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test measures the number of different types of cells in your blood, including white blood cells responsible for fighting infections.
Blood Culture: This test involves taking a blood sample and culturing it in a laboratory to identify the presence of bacteria or fungi that may be causing an infection.
Serology Test: This test looks for the presence of antibodies in your blood produced by your immune system in response to an infection. Serology tests can help identify past or current infections, depending on the type of antibodies detected.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Test: This test detects the genetic material of viruses or bacteria in your blood, which can help identify the presence of an infection, even in very small amounts.
Can blood tests accurately detect all types of infections?
Blood tests are a valuable tool in detecting many types of infections, but they may not be able to detect all infections with equal accuracy. The accuracy of a blood test in detecting an infection depends on various factors, including the type of infection, the timing of the test, and the sensitivity and specificity of the test being used. False negatives or false positives can occur in blood tests, and further testing or clinical evaluation may be needed for confirmation.
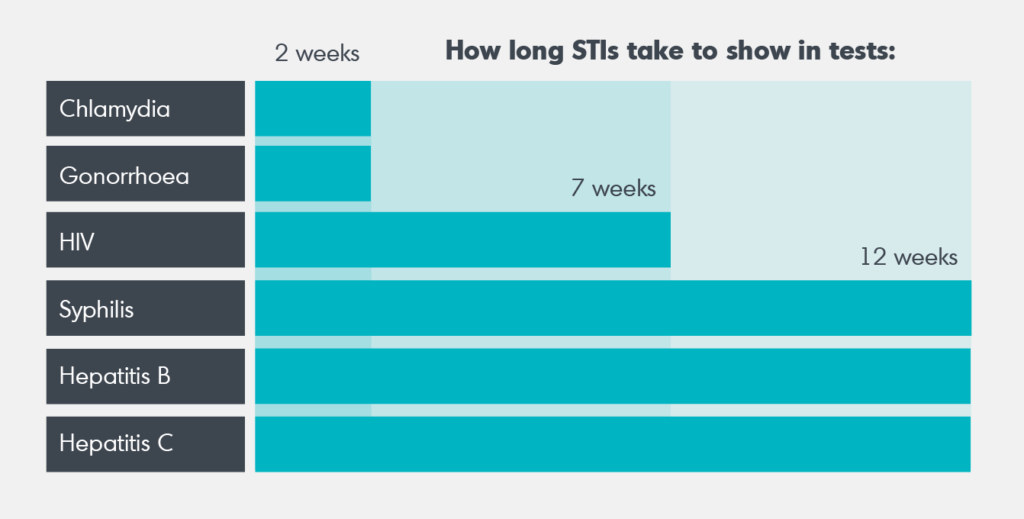
How long does it take for an infection to show up in a blood test?
The timing of when an infection will show up in a blood test can vary depending on the type of infection and the specific blood test being used. Some infections may appear in blood tests within a few hours or days of exposure, while others may take longer. For example, a blood culture may take several days to grow the organisms in the lab and provide results, while a PCR test for a viral infection may provide results within a few hours.
Can a blood test rule out an infection completely?
While blood tests can help detect infections, it’s important to note that they may not always be able to rule out an infection completely. False negatives can occur in blood tests, especially if the infection is in its early stages or the test has lower sensitivity.
Suppose you are experiencing symptoms of an infection. In that case, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider who may order additional tests or conduct a clinical evaluation to make an accurate diagnosis.
