Are you tired of constantly dealing with dry, itchy, and irritated skin caused by eczema? How to treat eczema naturally? Do you reach for over-the-counter creams and lotions only to find temporary relief or even worsening of your symptoms? If so, it’s time to explore the natural treatment options for eczema.
Eczema is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by red, inflamed, and itchy patches of skin that can be uncomfortable and unsightly. While eczema is not cured, natural remedies can help manage symptoms and promote healthy skin.
In this article, we will explore some of the most effective natural treatments for eczema. From diet and lifestyle changes to herbal remedies and essential oils, we will provide the tools to control your eczema and relieve your symptoms. So, whether you’re a long-time sufferer or just starting to experience eczema, read on to discover how to treat this condition naturally.
What is Eczema?
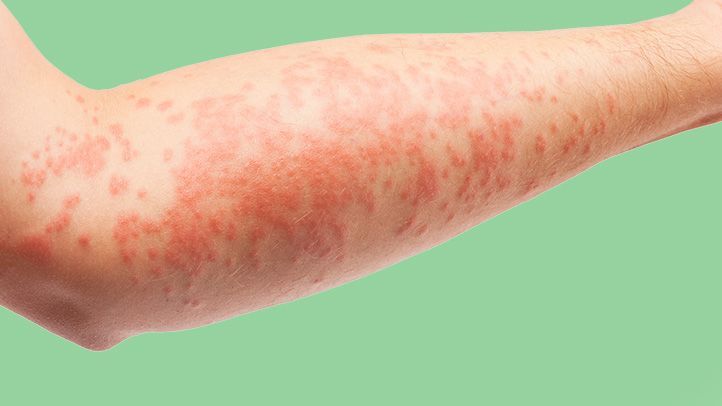
Eczema is a skin condition that is also known as atopic dermatitis. It is a chronic condition that causes skin inflammation, dryness, itching, and redness. Eczema can occur at any age but is more common in children. According to the National Eczema Association, approximately 31.6 million people in the United States have some form of eczema.
Also Read. 10 Best Foods for Healthy Skin | Improve Your Skin Naturally
Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema can cause a wide range of symptoms, including:
- Dry and itchy skin
- Redness and inflammation
- Small bumps or blisters that may leak fluid
- Thickened, cracked, or scaly skin
- Raw, sensitive, and swollen skin from scratching
If untreated, eczema can worsen, causing skin infections, permanent scars, and discolouration. Therefore, seeking treatment as soon as possible is important to prevent the condition from worsening.
Natural Remedies for Eczema
1. Coconut Oil
Coconut oil is a natural moisturizer that can help soothe dry and itchy skin caused by eczema. Coconut oil contains lauric acid, which has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. Applying coconut oil to the affected area can help reduce inflammation, soothe itching, and prevent skin infections.
To use coconut oil, warm it up slightly and apply it directly to the affected area. Repeat this process two to three times a day or as needed.
2. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is a succulent plant that is known for its medicinal properties. Aloe vera is a gel-like substance rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Aloe vera gel to the affected area can help soothe the skin, reduce inflammation, and promote healing.
Cut a leaf from the plant and extract the gel to use aloe vera. Apply the gel directly to the affected area and leave it on for 15-20 minutes. Rinse off the gel with cool water and repeat the process two to three times a day.
3. Oatmeal

Oatmeal is a natural remedy to help soothe itchy and inflamed skin caused by eczema. Oatmeal contains compounds called avenanthramides, which have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Applying oatmeal to the affected area can help reduce inflammation, soothe itching, and promote healing.
To use oatmeal, add a cup of finely ground oatmeal to a warm bath and soak for 15-20 minutes. Alternatively, you can make a paste by mixing oatmeal with water and applying it directly to the affected area. Leave the paste on for 10-15 minutes and rinse with cool water. Repeat the process two to three times a day.
4. Witch Hazel
Witch hazel is a natural astringent that can help soothe itchy and inflamed skin caused by eczema. Witch hazel contains tannins, which have astringent and anti-inflammatory properties. Applying witch hazel to the affected area can help reduce inflammation, soothe itching, and prevent skin infections.
To use witch hazel, apply a small amount to a cotton ball and dab it onto the affected area. Repeat the process two to three times a day or as needed.
5. Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is a natural remedy with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making it a useful treatment for eczema. Applying tea tree oil to the affected area can help reduce inflammation, soothe itching, and prevent skin infections.
To use tea tree oil:
- Mix a few drops with a carrier oil, such as coconut oil, and apply it directly to the affected area.
- Repeat this process two to three times a day or as needed.
- Note that tea tree oil can irritate some people, so it’s important to patch test before using it on larger areas of skin.
Is milk bad for eczema?
There is no definitive answer to whether milk is bad for eczema, as the relationship between the two can vary depending on the individual. Eczema is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. While no known cure for eczema exists, certain triggers can aggravate the condition and lead to flare-ups. Some people with eczema have reported that consuming dairy products like milk, cheese, and yoghurt can worsen their symptoms. However, the scientific evidence regarding the relationship between milk and eczema is mixed.
One possible reason why milk may be bad for eczema is that it contains a protein called casein, which some people may be allergic to. Allergic reactions to casein can cause skin irritation, hives, and other symptoms like eczema. In addition, milk also contains lactose, which is a type of sugar that some people may have difficulty digesting. Lactose intolerance can cause digestive problems, such as bloating, gas, and diarrhoea, triggering eczema flare-ups.
On the other hand, milk is also a good source of nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin D, which are important for maintaining healthy skin. Some studies have even suggested that consuming dairy products may protect against eczema. For example, a study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that children who consumed milk and dairy products during infancy had a lower risk of developing eczema later in life.
In summary, the relationship between milk and eczema is complex and can vary depending on the individual. While some people with eczema may find that consuming dairy products worsens their symptoms, others may not experience any adverse effects. Suppose you suspect that milk or other foods are triggering your eczema flare-ups. In that case, keeping a food diary and consulting with a healthcare professional to identify potential triggers and develop a personalized treatment plan may be helpful.
What fruits fight eczema?

Eczema is a common skin condition that causes itchy, inflamed, and irritated skin. While many treatments are available, including topical creams and medications, certain fruits may also help manage eczema symptoms. Here are some fruits that have been found to fight eczema potentially:
Berries:
Berries such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries are high in antioxidants, which can help reduce inflammation. Inflammation is a common trigger for eczema, so incorporating more berries into your diet could be helpful.
Avocado:
Avocado is high in healthy fats, which can help hydrate and nourish the skin. Dry, irritated skin often worsens eczema, so adding more healthy fats to your diet could help improve eczema symptoms.
Apples:
Apples are rich in quercetin, a flavonoid with anti-inflammatory properties. Eating apples and other quercetin-rich foods helps reduce inflammation, improving eczema symptoms.
Papaya:
Papaya is high in vitamin C, which can help boost the immune system and reduce inflammation. Additionally, papaya contains papain, an enzyme found to help soothe irritated skin.
While incorporating these fruits into your diet may help manage eczema symptoms, it’s important to remember that everyone’s body is different. If you have eczema, you should talk to your doctor or dermatologist about the best treatment options.
Conclusion!
In conclusion, much research shows that people with skin conditions tend to have poor nutrition. This can cause many problems, from inflammation to breakouts to skin discolouration. Eating a healthy diet rich in vegetables and fruits, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants has been proven to improve skin health greatly. If you are dealing with a skin condition, eat a balanced diet, take supplements, and use topical treatments and remedies.
FAQs!
What cures eczema fast?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as eczema can vary widely in severity and response to treatment. However, some common methods for managing eczema symptoms include:
Using moisturizers regularly to keep skin hydrated
Avoiding harsh soaps and detergents that can dry out the skin
Taking warm (not hot) baths or showers
Applying topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching
Using wet dressings or bandages to help soothe and heal skin
Taking oral antihistamines to reduce itching and swelling
It’s important to note that what works for one person may not work for another, and some people may need more intensive treatments such as phototherapy or systemic medications.
Can eczema be cured naturally?
There is no known cure for eczema, but some natural remedies may help to manage symptoms. These include:
Using natural moisturizers such as coconut oil, shea butter, or aloe vera
Taking lukewarm oatmeal baths to soothe and hydrate skin
Applying a cold compress to reduce itching and inflammation
Drinking plenty of water to keep skin hydrated
Using natural anti-inflammatory agents such as turmeric or ginger
Avoiding triggers such as certain foods, stress, or allergens
It’s important to note that natural remedies may not be as effective as prescription treatments, and some may even cause skin irritation or allergic reactions. Always talk to your healthcare provider before trying any new treatment or remedy.
What is the root cause of eczema?
The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it’s thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some possible triggers or risk factors include:
Genetics: Eczema tends to run in families, and certain genetic mutations may increase the risk of developing the condition.
Immune system dysfunction: People with eczema may have an overactive immune system that responds excessively to irritants or allergens.
Environmental factors: Exposure to certain irritants or allergens such as soaps, detergents, pollen, or dust mites can trigger or worsen eczema symptoms.
Stress: Emotional stress or anxiety can sometimes trigger or exacerbate eczema symptoms.
Dry skin: People with dry skin may be more prone to developing eczema, as the condition is characterized by skin that is dry, itchy, and prone to cracking or bleeding.
What foods to avoid if you have eczema?
While there is no definitive list of foods to avoid if you have eczema, some people may find that certain foods trigger or worsen their symptoms. Some common foods that may be problematic for people with eczema include:
Dairy products: Some people with eczema may be sensitive to dairy, triggering inflammation and itching.
Gluten: Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, and some people with eczema may be sensitive to it.
Eggs: Some people with eczema may have an egg allergy or sensitivity, which can cause skin inflammation and itching.
Nuts: Some people with eczema may be allergic to certain types of nuts, such as peanuts or tree nuts, which can cause skin irritation and itching.
Processed foods: Highly processed foods that contain additives, preservatives, or artificial flavours may trigger or exacerbate eczema symptoms in some people.
